What is the point of statistics when I need only average?
This is not entirely true.
For example, most people have two legs, someone has only one leg. When the average number of legs of all people is made, it turns out that most people have an above-average number of legs (the average is less than 2, because no one has three legs).
For this case, it is better to use another method of calculating the middle value.
In addition to the arithmetic average, we know two other frequently used means. MODE and MEDIAN
What is AVERAGE?
A number that is calculated by adding quantities together and then dividing the total by the number of quantities.
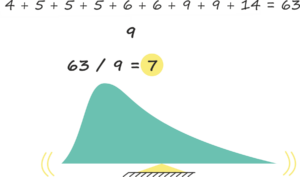
What is MEDIAN?
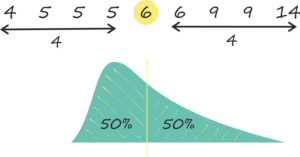
To find out its value, it is necessary to sort the values from the lowest to the highest – the value in the middle is the median. This is the best way to find the average value when one value in the whole is much higher or lower than the other values.
What is MODE?
It is the most recurring value in the data formula. In some cases, it may be more useful than the average or median. For example, if you want to know which cake is the best selling.
NORMAL (GAUSS) DISTRIBUTION
It is the most important and most common distribution of data in nature, society, etc. For example, if you ask about 200 random people, you divide them into groups 120-130, 130-140, 140-150 cm … and you calculate the number of people for each group, you can draw it in such a graph (HISTOGRAM).
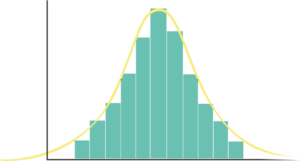
If you have a mound, it means that this data has a normal distribution. You will find it in many common cases that you can measure (height, weight, IQ, test results), but not in data that you just come up with. This means that there are the most cases around the average, and the further you move away from it (right or left), the fewer. And why is it called normal? Because that’s how it’s normal in nature.
The most often distribution
Normal distribution

Less known distribution
Paranormal distribution